Preventive medicine
What is preventive medicine?
The aim of modern medicine is not simply to treat illnesses once they have become manifest, but ideally to prevent them from developing or to delay their onset, in order to improve quality of life and ensure better health, even in later life. As the saying goes, prevention is the best cure.
There are three types of prevention:
Primary prevention aims to preserve health or prevent disease. It intervenes before damage, illness or irregular behaviour starts to occur and looks for the causes and risk factors that could lead to it.
Secondary prevention focuses on early detection and treating diseases. This approach aims to ensure that an illness does not worsen or become chronic.
Tertiary prevention aims to slow the progression of existing diseases or to prevent complications.
Primary prevention is of vital importance for a number of reasons:
This is often more effective and less costly than treating it once it has appeared.
By avoiding suffering, disability or even death.
Adopting healthy, positive lifestyle habits to maintain physical and mental health, well-being and independence over the years.
Examples of primary prevention

Informing the public about the risks associated with smoking, alcohol consumption and an unbalanced diet can lead to behavioural changes that are beneficial to health.
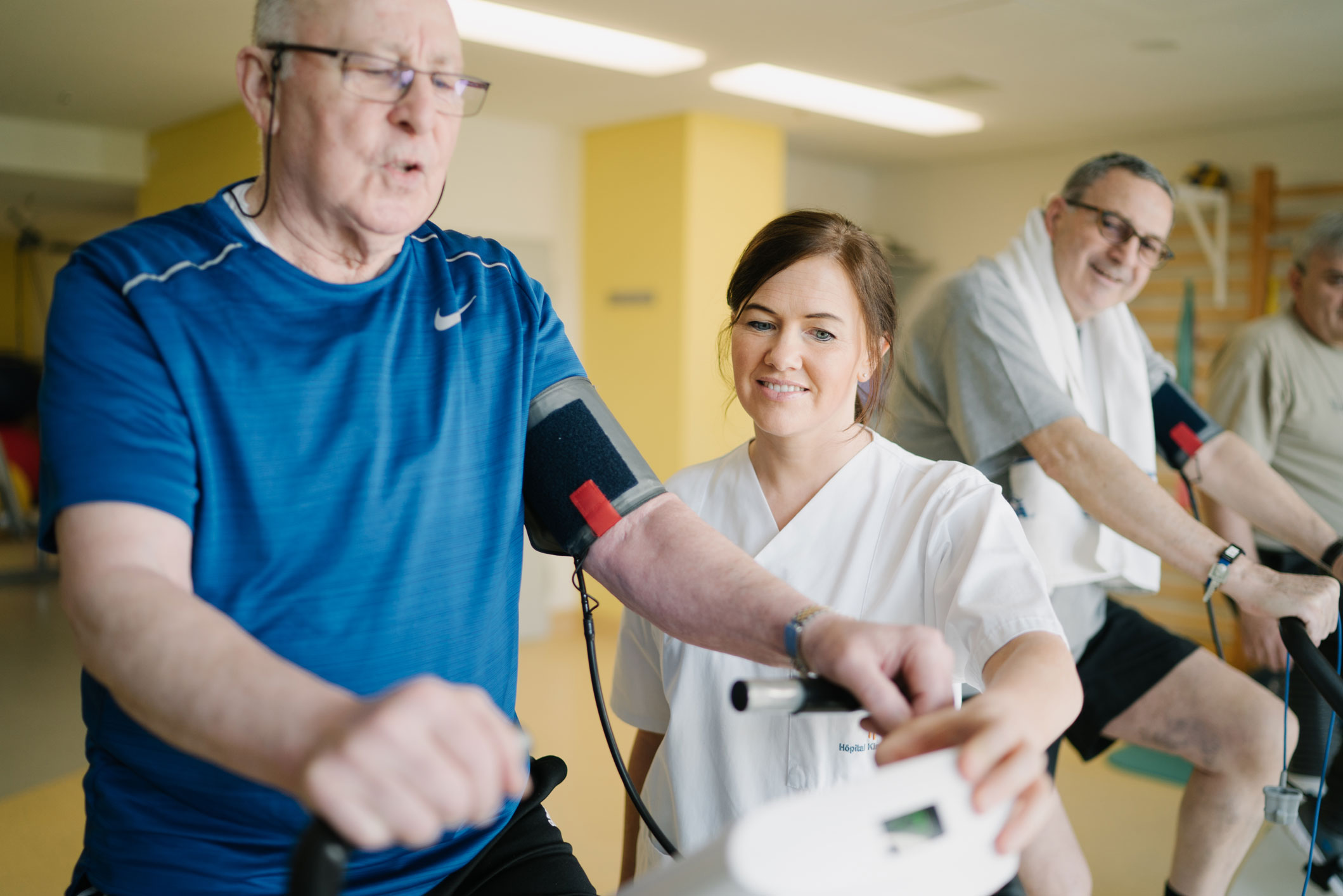

Encouraging people to engage in regular physical activity can prevent a large number of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and certain cancers.
The challenges of primary prevention
Although primary prevention has many advantages, its implementation faces several challenges:
-
Cultural and social resistance
In some cultures or social groups, preventive measures may be seen as unnecessary.
-
Initial cost
Prevention programs often require an initial investment.
-
Evaluation difficulties
The benefits of primary prevention can take time to become apparent, making it difficult to assess the effectiveness of a preventive measure in the short term.
of patients have one or more risk factors or illnesses following a check-up.
The main risks are being overweight or obese, physical inactivity, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, diabetes and hypertension, vitamin D deficiency, and skin, gynaecological or prostate cancer.
Help us better understand your needs so that we can provide you with personalised advice
Quickly and easily to consult our specialists
Receive a full, detailed check-up of your state of health and personalised results